Plasma/SerumCell-FreeCirculatingandViralNucleicAcidPurificationMaxiKit
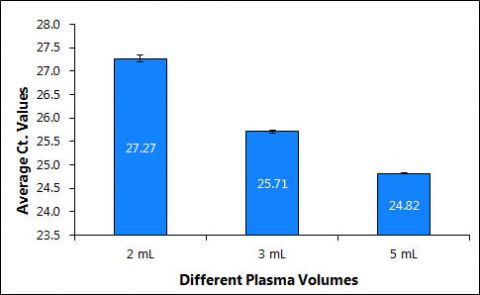
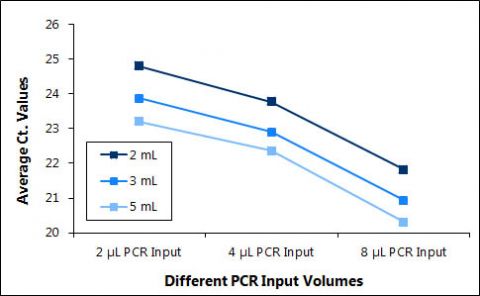
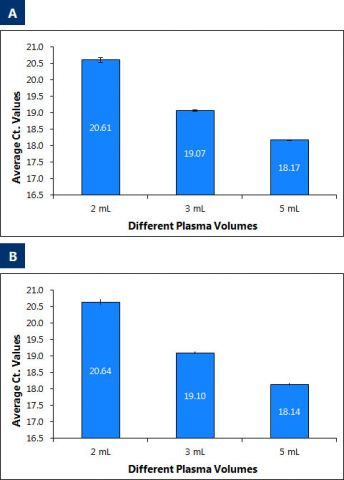
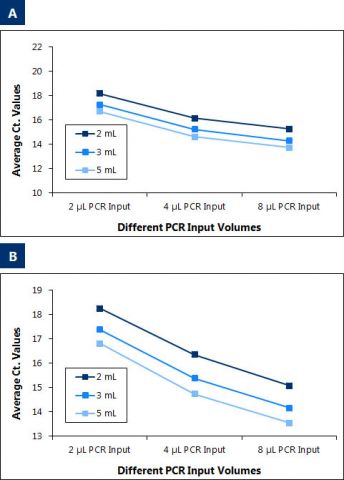
Thiskitprovidesafast,reliableandconvenientmethodtopurifyandconcentratehighquality,highpurityandinhibitor-freecell-freecirculatingDNA,circulatingincludingexosomalRNAaswellasviralDNA/RNAfromfreshorfrozenserumorplasmasamplespreparedfrombloodcollectedoneitherEDTAorCitratefromvolumesrangingfrom2mLto5mL.PlasmasamplespreparedfrombloodcollectedonheparinshouldnotbeusedasheparincansignificantlyinterferewithmanydownstreamapplicationssuchasRT-PCR
Thefirstcolumnwillhandlethelargevolumeinputofbodilyfluidsthatisfollowedbyaconcentrationonaminicolumnforafinalelutionof50µLto100µL.Allcomponentsforthepurificationareprovidedinoneconvenientandfastkitfortheeasyprocessingofsmallinputvolumesofbodilyfluids.Foraschematicworkflowoftheprotocolclick here.
Thepurifiedplasma/serumcirculatingandviralnucleicacidisfullycompatIBLewithalldownstreamapplicationsincludingPCR,qPCR,methylation-sensitivereversetranscriptionqPCR,reversetranscriptionPCR,methylation-sensitivePCRandSouthernBlotanalysis,Northernblotting,RNaseprotectionandprimerextension,expressionarrayassays,andNGS.
Background
Plasma/serumcell-freecirculatingandviralnucleicacidhasthepotentialtoprovidebioMarkersforcertaincancersanddiseasestatesaswellasforthedetectionofviralinfection.Currently,significantadvancementsarebeingmadeinutilizingcfc-DNAasbiomarkersfortheearlydiagnosis,prognosisandmonitoringoftherapyforseveralcancertypesandautoimmunediseases.Cell-freemitochondrialDNA(cfmtDNA)isalsounderinvestigationforitsclinicalsignificance.Thiscfc-DNAisusuallypresentasshortfragmentsoflessthan1000bp.Inaddition,cell-freefetalDNAhasbeenwidelyusedasanon-invasivemethodforprenataldiagnosisincludingearlyidentificationoffetalsex,geneticstudiesforfamiliesathighriskforinheritedgeneticdisorders.screeningforRhesusfactor,screeningforaneuploidyandidentificationofpreeclampsiaExosomesare40-150nmmembranevesicles,whicharesecretedbymostcelltypes.Exosomescanbefoundinsaliva,blood,urine,amnioticfluidandmalignantasciticfluids,amongotherBIOLOGicalfluids.Evidencehasbeenaccumulatingrecentlythatthesevesiclesactascellularmessengers,conveyinginformationtodistantcellsandtissueswithinthebody.Theseexosomesmayplayafunctionalroleinmediatingadaptiveimmuneresponsestoinfectiousagentsandtumours,tissuerepair,neuralcommunicationandtransferofpathogenicproteins.ForthisreasonexosomalRNAsmayserveasbiomarkersforvariousdiseasesincludingcancer.AstheRNAmoleculesencapsulatedwithinexosomesareprotectedfromdegradationbyRNAsestheycanbeefficientlyrecoveredfrombiologicalfluids,suchasplasmaorserum.
Protocol